
What is Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery or robot-assisted surgery is a minimally invasive surgery that unites advanced computer technology, high-tech equipment, and integrated lighting. The high-tech equipment used for advanced surgeries would be inadequate without integrated lighting.
Robot-assisted surgery is an ever-evolving technology that holds benefits for the patient and physician. Technological advances have increased the types of procedures that are performed, such as minimally invasive surgeries. These surgeries allow the surgeon to create smaller incisions which results in faster recovery times and less pain for a patient.
As a world-class lighting technology innovator, our dedication inspires us to stay on top of the latest minimally invasive surgery techniques and technological advancements in the market. This article covers traditional (open) surgery procedures vs. robotic-assisted surgery, the growth of robotic technology, and the high-tech equipment used for advanced operations with integrated lighting.
What is Robotic Surgery?
Surgeries and procedures that once required larger incisions and longer recovery times are now minimally invasive. Robotic surgery or robot-assisted surgery is a minimally invasive surgery that integrates advanced computer technology.
James Renz, MD, PCI Surgeon and robotics team at Unity Point Health describes the process as:
"A very small 3D camera and dime-sized surgical instruments are placed inside the patient through tiny incisions. The camera gives the surgeon a magnified 360 degree view of the operative field.
Using the console's hand and foot controls, the surgeon remotely moves robotic arms attached to surgical instruments. A second surgeon is positioned at the operating table to confirm the correct placement of the surgical instruments."
The robotic instruments are able to bend and rotate freely and independently in up to 7 different degrees of motion.
The robotic surgeries are designed towards smaller incisions, which often result in less pain and fewer complications. The quid pro quo is the surgeon must perform these surgeries in narrower and deeper cavities, where visualization becomes demanding.
It's important to note not all surgeries can be performed robotically. And not all patients are candidates for surgical robotics.
Quick History of Robotic Technology
In the mid-1980's, computer technology and design engineering began to merge with the field of robotics. The past 30+ years have seen an explosion in the industry, with a global forecast of $11.4 billion by the year 2020.
The timeline below highlights the growth of robotic technology and respective surgeries through the years.
1985 Robotic arm helps with surgery. The PUMA 560 (large-armed system) robotic surgical arm is used in the first documented use of a robot-assisted surgical procedure.
1987 The 1985 robotic surgery lead to the first laparoscopic procedure involving a robotic system, a cholecystectomy, in 1987.
1988 PROBOT, developed at Imperial College London, used for prostate surgery.
1990's AESOP system approved by the FDA for its endoscopic surgical procedure.
1992 ROBODOC is introduced. The robot was designed to help surgeons during hip replacement surgery.
2000 FDA approved the first comprehensive robotic system for laparoscopic surgery. The FDA approved the da Vinci Surgical System, which allowed the doctor to be across the room from the patient while directing the movements of the arms by control and a video display.
"This system offers the surgeon 7 degrees to freedom allowing the robotic arm to replicating exactly what the human arm could do". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4677089/
2001 Tele-surgery: Transatlantic cholecystectomy, the surgeon was located in NY, the patient was located in Strasburg.
2007 A computer-assisted surgical robot designed for neurosurgery - the neuroArm was developed.
2008 First brain surgery to remove a tumor through the use of MRI-compatible robotics.
2009 Largest multi-institutional study on the use of the da Vinci robotic surgical system.
2009 The latest model (da Vinci robotic surgical system) was released in April 2009, upgrading the imaging system to HD and also allowing for a second surgeon’s console which allows for the training of a less experienced surgeon.
2012 Single Port Robotic Surgery - Intuitive systems are coming out with a new single port system for robotic surgeries, a split-off of laparoscopic surgeries, where all three scopes will go through a port so there will be less trauma to the body.
2017 Robotic surgery statistics released by iData Research demonstrates that over 693,000 robotic-assisted procedures were performed in 2017 in the U.S.
Resources:
https://www.roboticoncology.com/history-of-robotic-surgery/
https://www.britannica.com/science/robotic-surgery#ref1225036
https://www.medicaldesignbriefs.com/component/content/article/mdb/features/25006
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4677089/
Difference Between Traditional, Laparoscopic, and Robotic Surgery
There are pros and cons to any type of surgery.
Traditional or Open Surgery is typically a type of surgery that requires a larger incision using a scalpel, or lancet. The incision can range from a few inches (3-4 inches) to very large depending on the procedure being performed.
Some surgeries still require traditional methods for access to larger areas and to accurately diagnose a condition. As new technologies come to fruition, procedures are considered based on the needs of the patient.
Laparoscopic surgery is the use of endoscopic equipment controlled by the surgeon's hand. The process takes its name from the laparoscope, "a slender tool that has a tiny video camera and light on the end. When a surgeon inserts it through a small cut and into your body, they can look at a video monitor and see what’s happening."
It typically uses smaller incisions (no more than a half-inch long). Because of the smaller cuts, most patients have a quicker recovery with smaller scars.
Robotic surgery takes it even a step further with miniaturized surgical instruments that fit through a series of quarter-inch incisions.
NYU Langone Health states "when performing surgery with the daVinci Si—the world’s most advanced surgical robot — these miniaturized instruments are mounted on three separate robotic arms, allowing the surgeon maximum range of motion and precision. The da Vinci’s fourth arm contains a magnified high-definition 3-D camera that guides the surgeon during the procedure."
David B. Samadi M.D., Robotic Oncology, agrees the advancement with the daVinci Surgery System,
"allows for less contact between exposed interior tissue and the surgical device, greatly reducing the risk of infection."
The video below created by Robotic Surgical Institute helps define traditional, laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
FAQ | Surgery Types
Woodlands Medical Specialists. "FAQ | Surgery Types". YouTube. February 26, 2014.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotic Surgery
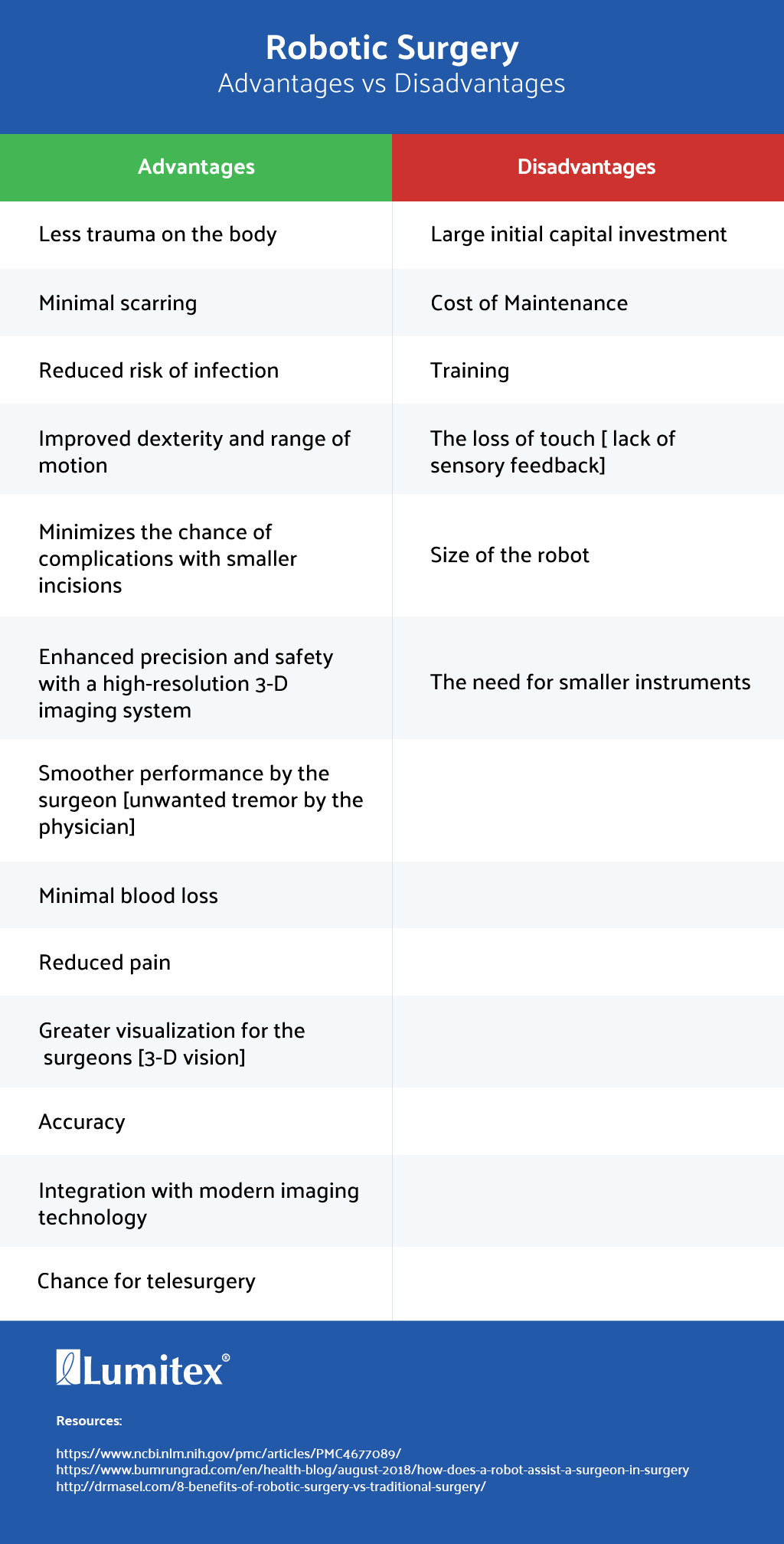
"You don’t only have to learn how to use the instrument, but you also need to learn how to perform the surgery." Dr. Orady
Equipment Used in Robotic Surgery
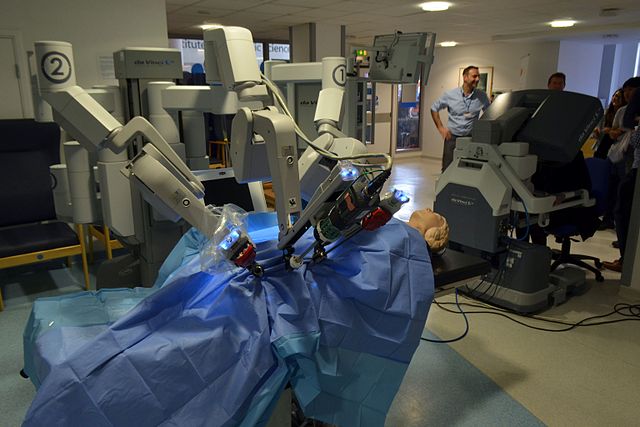
Image Credit: Cmglee [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Let's take a look at the most common and widely known da Vinci Surgical System. It is composed of 3 main parts:
1. Master console - computer console in an operating room. The surgeon sits in an ergonomically designed chair to control the robot from the main computer.
2. Electronic tower - An electronic tower holds the video, the light, a monitor for the assist and the insufflator.
3. Slave Robot - The robotics tower or slave robot is positioned over the patient and holds three or four arms.
source: Urology Robotic Surgery
In the da Vinci system, which evolved from the telepresence machines developed for NASA and the US Army, there are essentially 3 components: a vision cart that holds a dual light source and dual 3-chip cameras, a master console where the operating surgeon sits, and a moveable cart, where 2 instrument arms and the camera arm are mounted. [NCBI ]
Robotic surgery uses small tools attached to the robotic arm. Surgical cuts are smaller and allow the surgeon to insert instruments into the cavity.
MedlinePlus explains, "a thin tube with a camera attached to the end of it (endoscope) allows the surgeon to view enlarged 3-D images of your body as the surgery is taking place. The robot matches the doctor's hand movements to perform the procedure using the tiny instruments."
(reference: Muller CL, Fried GM. Emerging technology in surgery: Informatics, electronics, robotics. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2017:chap 15.)
The high-tech equipment used for advanced surgeries would be inadequate without integrated lighting.
Conclusion
Since the introduction of robotic surgery, many advances and achievements have been made in the industry. Analysts forecast the global robotic general surgery market to grow at a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 10.53% during the period 2017-2021.
Robotic surgical technology will be a significant part of the future of healthcare IT. Robotic assisted procedures will only continue to experience growth.
As a company, Lumitex who is in the medical space understands these trends and the impact it has on the healthcare industry. Lumitex can help design, develop and manufacture surgical illumination for your needs.





Comments